Cisco IOS eBGP (External) Protocol
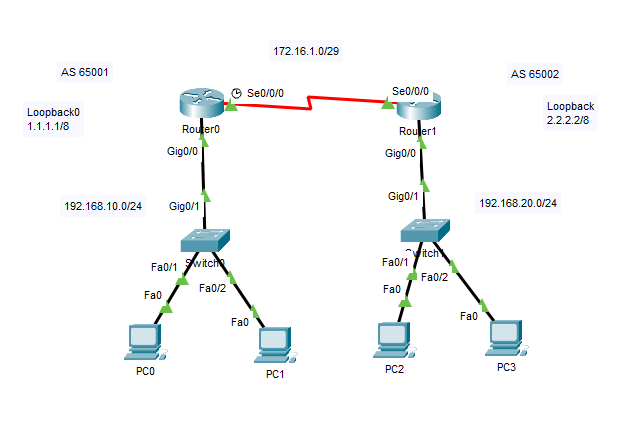
Network Topology
As of Cisco Packet Tracer 8.2 internal BGP (iBGP) is not supported only external BGP (eBGP) is supported. If you try and configure iBGP on Packet Tracer, you will see the following message.
So, in this example the focus will be on setting up eBGP between two separate autonomous systems.
Router0 Configuration Commands
Router0>enable
Router0#configure terminal
Router0(config)#interface serial 0/0/0
Router0(config-if)#ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.248
Router0(config-if)#no shutdown
Router0(config-if)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
Router0(config-if)#ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Router0(config-if)#no shutdown
Router0(config-if)#int Loopback 0
Router0(config-if)#ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0
Router0(config-if)#no shutdown
Router0(config-if)#exit
Router0#router bgp 65001
Router0(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.1.2 remote-as 65002
Router0(config-router)#network 1.1.1.1 mask 255.0.0.0
Router0(config-router)#network 192.168.10.0 mask 255.255.255.0
Router0(config-router)#no synchronization
Router1 Configuration Commands
Router1>enable
Router1#configure terminal
Router1(config)#interface serial 0/0/0
Router1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.248
Router1(config-if)#no shutdown
Router1(config-if)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
Router1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
Router1(config-if)#no shutdown
Router1(config-if)#int Loopback 0
Router1(config-if)#ip address 2.2.2.2 255.0.0.0
Router1(config-if)#no shutdown
Router1(config-if)#exit
Router1#router bgp 65001
Router1(config-router)#neighbor 172.16.1.1 remote-as 65001
Router1(config-router)#network 2.2.2.2 mask 255.0.0.0
Router1(config-router)#network 192.168.20.0 mask 255.255.255.0
Router1(config-router)#no synchronization
A Special Word about the No Synchronization Command
The site BGPExpert has an excellent explanation of what the no synchronization command is and what is does.
Check BGP Configuration
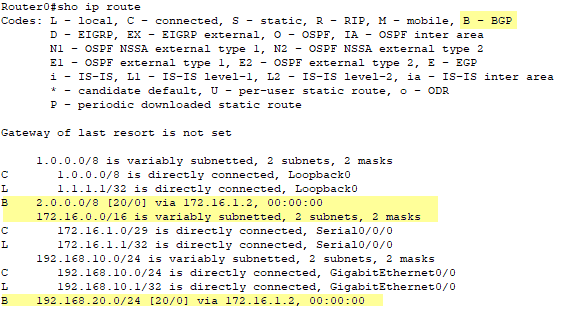
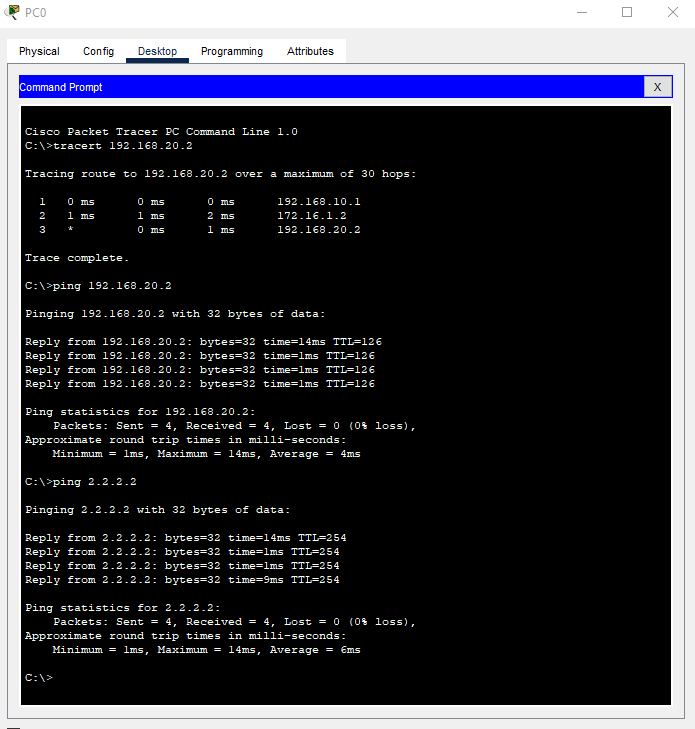
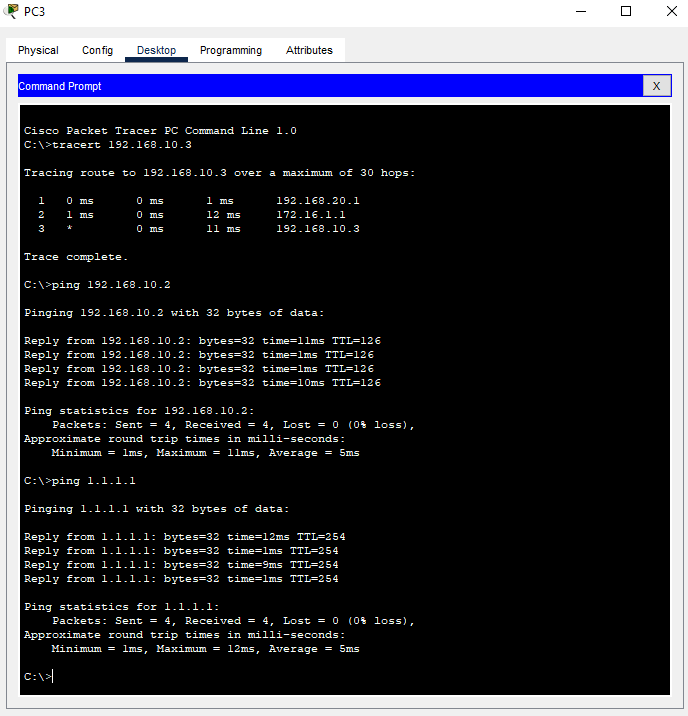
Router0#show ip route
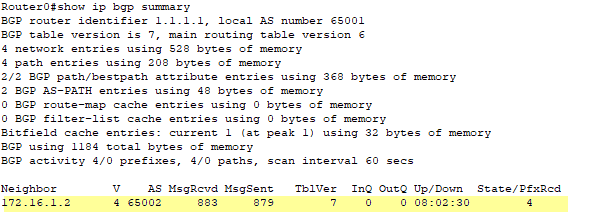
Router0#show ip bgp summary
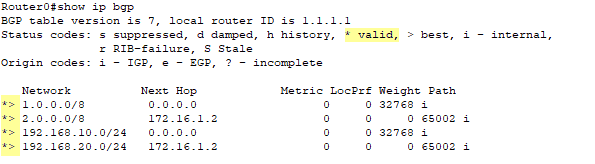
Router0#show ip bgp
Ping and Tracert Connectivity Tests
More Notes on BGP
- BGP communicates using TCP port 179
- BGP can form neighbor adjacencies with directly connected routers, which isn't a surprise as other routing protocols do that. But BGP can also form neighbor adjacencies with routers multiple hops away.
Directly Connected BGP Neighbors |
Multihop BGP Neighbors |
| BGP will use the Arp table to locate the Layer 2 address of the peer. | BGP will use routing table information to find the peer's IP address. |
- BGP is a path-vector routing protocol meaning it uses path attributes that are associated with each network path when selecting the best route. This also helps ensure that the path taken is loop free.
- BGP path attributes are defined in RFC 4271 (January 2006 release date).
- RFC 1654 defined BGP and termed it an Inter-Autonomous System routing protocol.
- The 'AS' in the network topology is short for Autonomous System. An Autonomous System is. 'the entire routing domain controlled by a company, ISP, or other organization.
- Inter-Autonomous means that BGP is able to route packets across organizations' routing domains. This makes BGP perfect for the routing of the Internet.
- An organization requests an Autonomous System Number (ASN) from the Internet Service Provider (ISP) or more typically from the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority IANA.
- The ASN is a 16-bit or 32-bit number.
- 32-bit ASN length provides for 4,294,967,295 unique ASNs.
- There are private ASNs that any organization can use. These are similar in concept to the private IP ranges that any organization can use internally listed below.
- Class A 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
- Class B 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
- Class C 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255
Private 16-bit ASN Range |
Private 32-bit ASN Range |
| 64,512 - 65,535 | 4,200,000,000 - 4,294,967,294 |